Overview
The rate of reaction is the change in the amount of a reactant or product per unit time. Reaction rates are therefore determined by measuring the time dependence of some property that can be related to reactant or product amounts. Rates of reactions that consume or produce gaseous substances, for example, are conveniently determined by measuring changes in volume or pressure.
The mathematical representation of the change in the concentration of reactants and products, over time, is the rate expression for the reaction. The brackets indicate molar concentrations, and the symbol delta (Δ) indicates “change in.”
For example, the concentration of hydrogen peroxide, H2O2, in an aqueous solution changes slowly over time as it decomposes according to the equation:
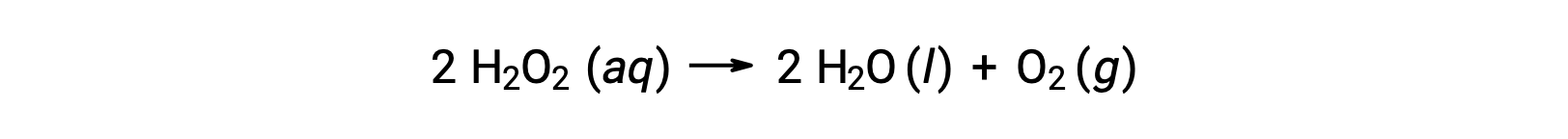
The rate at which the hydrogen peroxide decomposes can be expressed in terms of the rate of change of its concentration:

Thus, [H2O2]t1 represents the molar concentration of hydrogen peroxide at time t1; likewise, [H2O2]t2 represents the molar concentration of hydrogen peroxide at a later time t2; and Δ[H2O2] represents the change in molar concentration of hydrogen peroxide during the time interval Δt (that is, t2 − t1). Since the reactant concentration decreases as the reaction proceeds, Δ[H2O2] is a negative quantity. Reaction rates are, by convention, positive quantities, and so this negative change in concentration is multiplied by −1.
Average reaction rate and instantaneous reaction rate
Reaction rates vary with time and decrease as the reaction proceeds. An average reaction rate over a time interval can be calculated using the concentrations at the beginning and end of this period, over which the reaction rate is changing. At any specific time, the rate at which a reaction is proceeding is known as its instantaneous rate. The instantaneous rate of a reaction at “time zero,” when the reaction commences, is its initial rate.
The instantaneous rate of a reaction may be determined by one of the two ways. If experimental conditions permit the measurement of concentration changes over short time intervals, then the computation of average rates provide reasonably good approximations of instantaneous rates. Alternatively, a graphical procedure may be used. For instance, in the hydrogen peroxide decomposition example, by plotting the concentration of hydrogen peroxide against time, the instantaneous rate of decomposition of H2O2 can be computed at any time ‘t’ from the slope of a tangent drawn to the curve at that time.
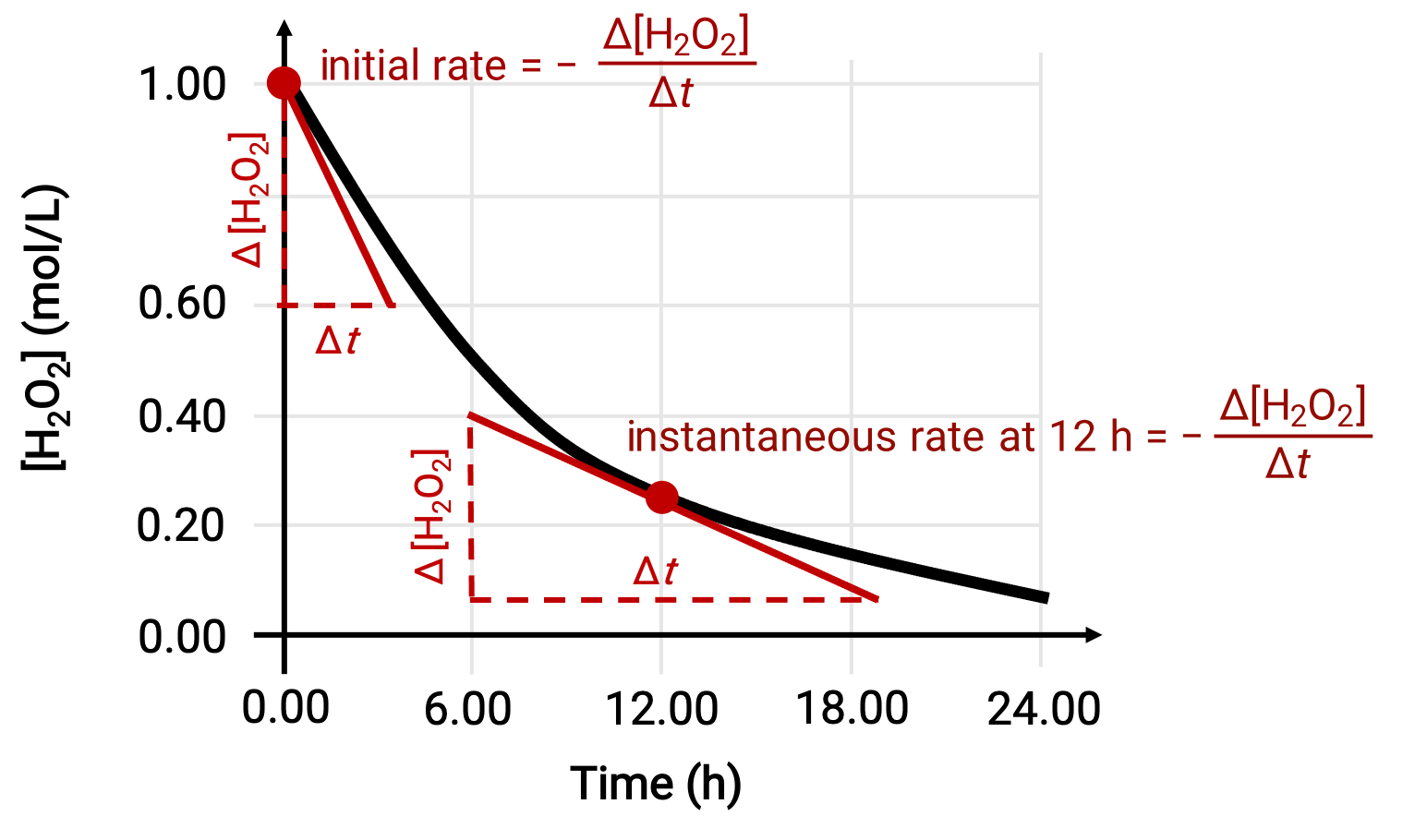
This graph shows a plot of concentration versus time for a 1.000 M solution of H2O2. The rate at any time is equal to the negative of the slope of a line tangent to the curve at that time. Tangents are shown at t = 0 h (“initial rate”) and at t = 12 h (“instantaneous rate” at 12 h).
Relative Rates of Reaction
The rate of a reaction may be expressed as the change in concentration of any reactant or product. For any given reaction, these rate expressions are all related to one another according to the reaction stoichiometry. The rate of the general reaction aA ⟶ bB can be expressed in terms of the decrease in the concentration of A or the increase in the concentration of B. These two rate expressions are related by the stoichiometry of the reaction, where:
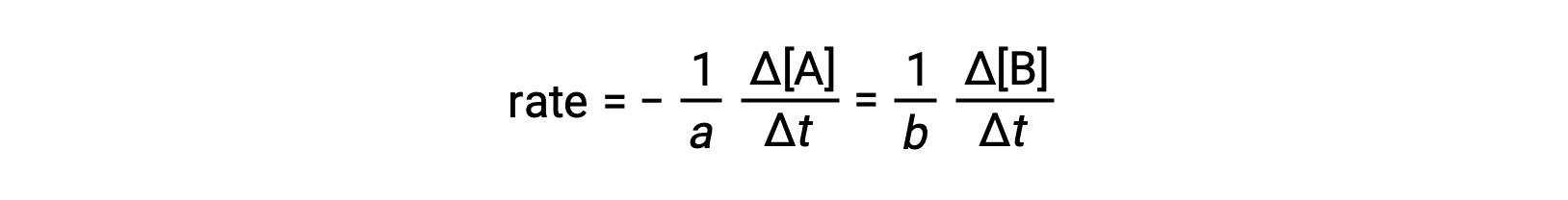
Note that a negative sign has been included as a factor to account for the opposite signs of the two amount changes (the reactant amount is decreasing while the product amount is increasing).
This text is adapted from Openstax, Chemistry 2e, Chapter 12 Introduction and Openstax, Chemistry 2e, Section 12.1: Chemical Reaction Rates.
Procedure
A chemical reaction involves the chemical transformation of reactants into products. As the reaction progresses, the concentration of reactants decreases while the concentration of products increases. This variance in concentrations of reactants and products can be plotted in a graph as a function of time.
The speed at which a reaction progresses is called the reaction rate. It measures the rate of reactants’ disappearance or the rate of products’ appearance and is expressed in units of molarity-per-second.
The average reaction rate can be calculated from the change in concentrations of reactants or products during a specific period of time. The molar concentration value is denoted in brackets, t stands for the period of time, and the delta symbol represents ‘change in’.
Since reactants are depleted during a chemical reaction, the value of concentration change of reactants is always negative. Therefore, a reaction rate calculated in terms of reactants is supplemented by a negative sign, to make the overall value positive.
The reaction rate is not uniform throughout a reaction. The rate at the start of the reaction, at ‘time-zero’, is called the initial reaction rate. As the concentrations of reactants reduce, the reaction rate decreases, or the reaction slows down.
The reaction rate at a given time point, or the instantaneous reaction rate, is measured by calculating the slope of a tangent drawn to the reaction curve, for either reactants or products, at the time of interest.
The slope value or the instantaneous rate at a specific time-point is equal for all reactants and products.
The reaction rate of a chemical reaction also reflects the actual stoichiometric coefficients of reactants and products.
So, for any balanced reaction, where a moles of A reacts with b moles of B, producing c moles of C and d moles of D, the reaction rate can be expressed and calculated using the generic formula: −1/a × Δ[A]/Δt = −1/b × Δ[B]/Δt. These values are the same as +1/c × Δ[C]/Δt, which is the same as +1/d × Δ[D]/Δt.
Determining reaction rates is fundamental to studying chemical kinetics, which helps to understand how quickly a drug, catalyst, or a synthetic reaction works so that it can be better controlled and optimized in its function.